COVID19 and Black Fungus: Everything you need to know about the rising mucormycosis infections in India
In the second wave of COVID19, many people recovering from COVID-19 have been afflicted with black fungus – or mucormycosis – disease, which may become fatal. What is mucormycosis? Who is at risk? What is the treatment? Read on to find out.

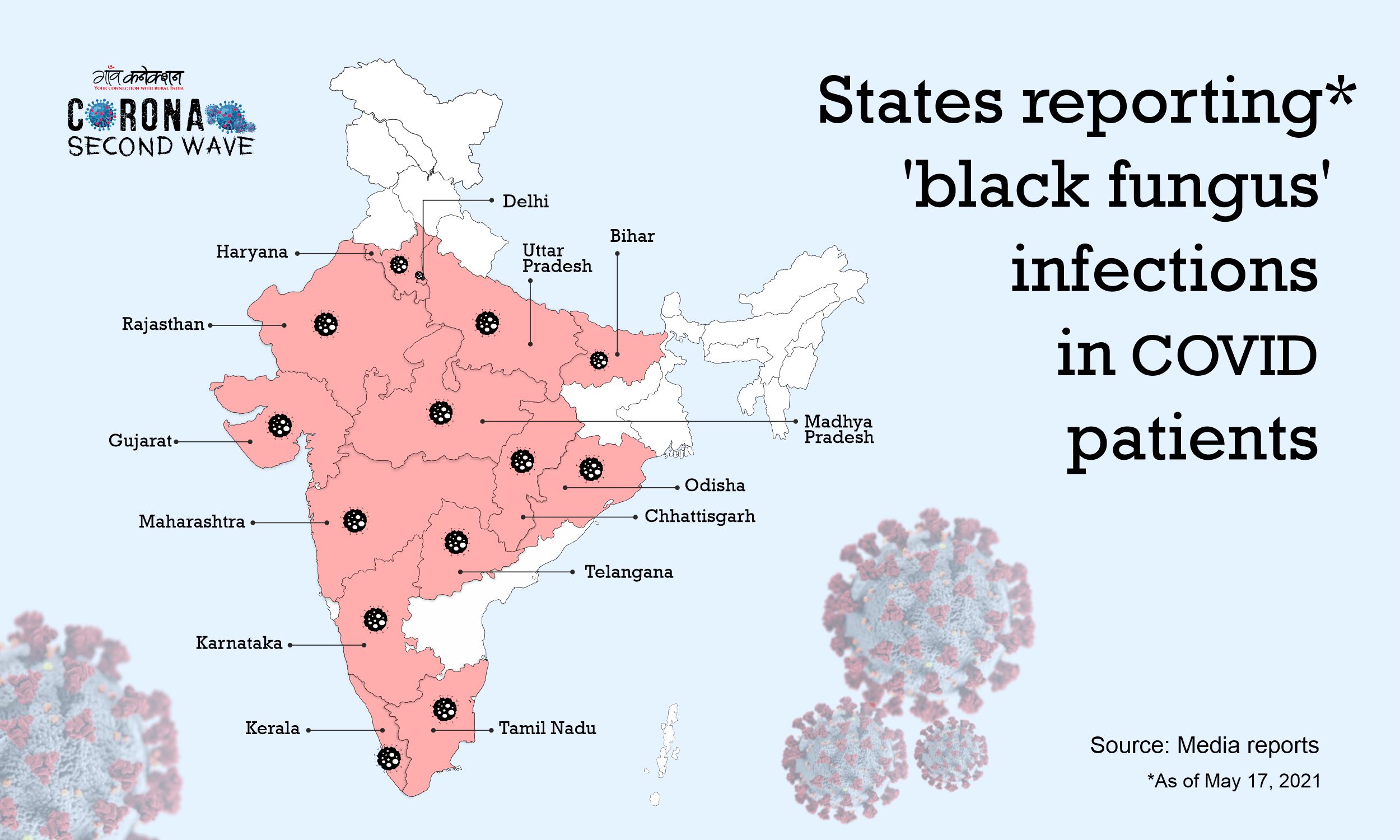
Amidst the uncontrolled rise in COVID19 cases across the country, another worrying infection, called Mucormycosis, or Black Fungus is rearing its ugly head. Several states including Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, and Gujarat, are reporting the infection.
As per a recent advisory issued by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), Mucormycosis — a fungal infection detected in COVID-19 patients — is likely to turn fatal if left untreated.
What is Mucormycosis?
Mucormycosis is a fungal infection that mainly affects people who are on medication for other health problems, and have a reduced ability to fight environmental pathogens.
The sinuses or lungs of such individuals get affected when they inhale fungal spores from the air.
The symptoms of Mucormycosis include:
- Pain and redness around the eyes and/or nose
- Fever
- Headache
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
- Blood in vomit
- Altered mental state
Prevention
- Wearing masks in dusty environments.
- Wearing shoes, long trousers, long sleeved-shirts and gloves while handling soil (gardening), moss or manure.
- Maintaining personal hygiene including a thorough scrubbing while bathing.
Watch out for:
- Sinusitis-nasal blockade or congestion.
- Nasal discharge (blackish/bloody).
- Local pain on the cheek bone.
- Pain, numbness or swelling on one side of the face
- Toothache.
- Blurred or double vision with pain.
- Chest pain, Difficulty in breathing.
Who is at risk?
- Those with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
- immunosuppression by steroids.
- Who have had a prolonged stay in an Intensive Care Unit
- Those with comorbidities – especially post transplant/malignancy.
Measures to take:
- Control hyperglycemia.
- Monitor blood glucose level post Covid-19 discharge, and also if diabetic.
- Use steroids judiciously, paying attention to correct timing, dose and duration.
- Use clean, sterile water for humidifiers during oxygen therapy.
- Use antibiotics/antifungals judiciously.
What not to do?
- Do not ignore warning signs and symptoms.
- Do not consider all cases with blocked nose as cases of bacterial sinusitis, particularly in the context of COVID19 patients on immunomodulators.
- Do not hesitate to seek aggressive interventions such as tests like KOH staining, microscopy, culture, MALDI TOF, that can detect fungal etiology.
- Act promptly to initiate treatment
Managing the infection
- Control diabetes and diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Reduce steroids (if still on them) and discontinue them as soon as possible.
- Discontinue immunomodulating drugs.
Medical treatment
- Install peripherally inserted central catheter.
- Maintain adequate systemic hydration.
- Infuse normal saline intravenously before Amphotericin B infusion.
- Undergo anti-fungal therapy for at least 4-6 weeks.

